The latest Coronavirus pandemic has gotten a lot of attention. It’s easy to get perplexed since there’s so much misinformation and gossip floating around. We want to dispel any misconceptions and provide you with correct information in this blog. So let’s begin by learning more about the virus.
What is Coronavirus, exactly?
The common cold, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), and Middle East respiratory syndrome are all caused by the coronavirus family of viruses (MERS). In China, a new coronavirus epidemic broke out in 2019.
SARS-CoV-2, coronavirus disease 2019, and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) are some of the various names given to the coronavirus (COVID-19). Coronavirus is a virus that affects both people and animals. It’s possible that a virus that affects animals evolves into a new virus that infects people. These types of coronavirus are more dangerous since they may cause life-threatening pneumonia.
The following are the three most prevalent ailments caused by Corona virus:
SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome) is a life-threatening respiratory infection that was first found in China in 2002. Since 2002, there have been no new instances of this virus reported.
MERS (Middle East respiratory syndrome) – In 2012, Saudi Arabia was the first country to disclose this serious respiratory ailment. It spread to 27 nations from there, including the United States, where two cases were documented. The Arabian Peninsula was revealed to be the source of all of the instances.
Coronavirus illness 2019 (COVID-19) — the root of the conflagration in Wuhan in 2019 is travel from Hubei Province. The sickness has now spread to numerous nations throughout the globe, with some instances even being recorded in the United States. The Centers for Illness Control (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO) are keeping track of all disease updates (WHO).
What are the signs and symptoms of Coronavirus infection?
Coronavirus symptoms appear if you’ve been to locations where the virus is spreading or if you’ve been in touch with somebody who has traveled to such areas.
In general, coronavirus infections cause the following symptoms:
- Fever
- Cough
- Breathing problems
- Headache and sore throat
COVID-19 symptoms are less severe than those of SARS and MERS. If you haven’t been to these locations or come into contact with somebody from there, your symptoms might be caused by another virus, such as the flu.
Also know about the common side effects of the covid-19 vaccine.
Asymptomatic Transmission Poses a Risk
Our most powerful weapon in the battle against the epidemic is testing and social isolation. It is the only method to stop the virus from spreading and having an effect. The asymptomatic transmission of SARS-CoV-2, on the other hand, has made curbing the disease’s spread much more challenging. The fast spread of COVID-19 around the world is unequivocal proof of asymptomatic transmission. A person who is infected with COVID-19 but does not exhibit any symptoms is said to be asymptomatic. The term “asymptomatic transmission” refers to disease transmission from a person who has no symptoms. According to the Union Health Ministry of India, 80% of COVID-19 patients are asymptomatic or have moderate symptoms. Only during the early stages of the illness may COVID-19 spread from asymptomatic people. COVID-19 may be contracted from someone who does not seem to be unwell, has no severe symptoms, or just has a moderate cough.
As a result, even if you are asymptomatic, staying inside and reducing all potential risks of transmitting the virus is critical at this point. Sanitizing daily goods that may represent a high danger, such as cell phones, food packages, and newspapers, as well as limiting contact with potential hotspots, such as elevator buttons, doorknobs, handrails, and gym equipment, are all important to lower the likelihood of the virus spreading. Even if you are asymptomatic, people with reduced immunity owing to old age or those with underlying diseases such as Diabetes, Asthma, Cholesterol, or autoimmune disorders should be aware that it may be lethal.
Patients with a fever and respiratory symptoms who have an epidemiological relationship to COVID-19 should be treated with a high index of suspicion for the illness. The epidemiological link could be
- Travel to an outbreak area,
- Close contact with an individual with a confirmed or high risk of infection, or
- Close contact with an individual with respiratory symptoms who had been in a geographic location where an outbreak occurred within 14 days of the onset of symptoms.
Clinicians must remain up to current on the list of impacted nations and territories as the geographic region of engagement expands. Local transmission of illness happens after multiple generations of disease spread inside a nation, and patients may appear with no history of travel to a recognized epidemic region.
Patients who are critically sick may arrive to the emergency department from the community or may be transferred to the intensive care unit from another hospital. In such cases, a thorough investigation should be conducted to verify that proper screening and infection control steps are taken.

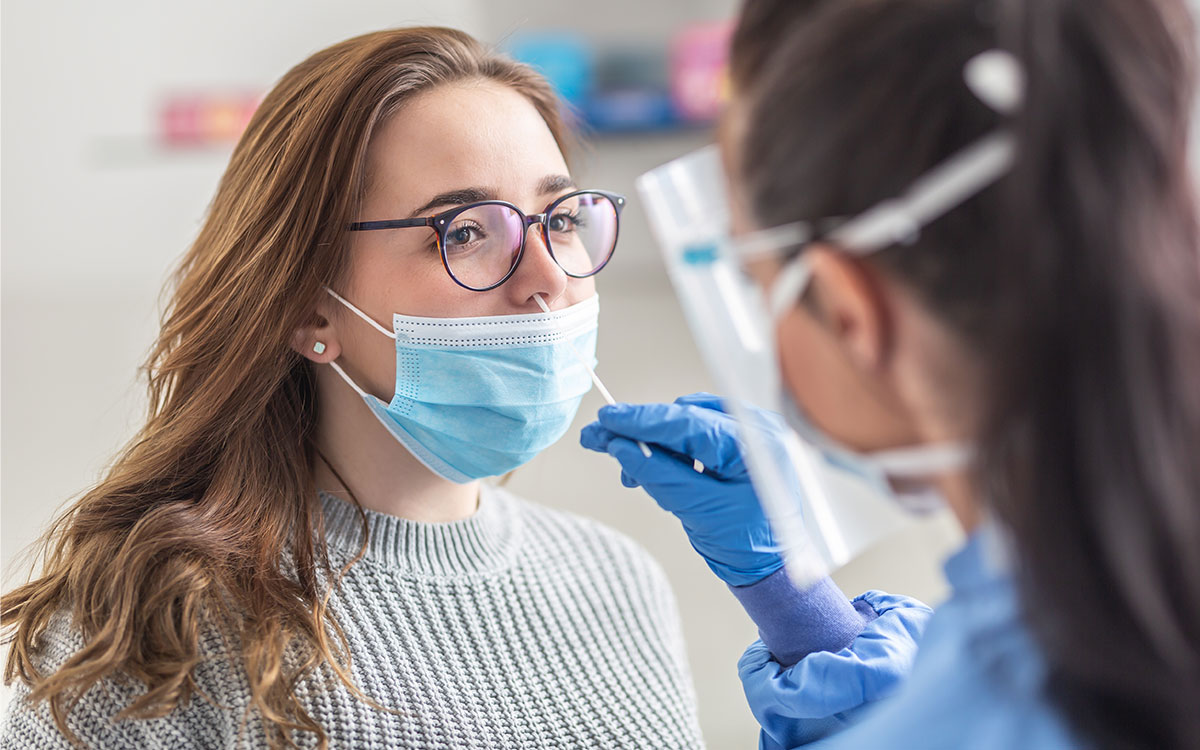
How can I obtain a Coronavirus test?
If you believe your symptoms are caused by the coronavirus, your healthcare practitioner may contact the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) or local health departments for testing instructions. Different types of Coronavirus tests are performed in specified laboratories, therefore you may be routed to one of them.
Coronavirus testing may be performed in a variety of ways:
- Swab Test – A specific swab is used to obtain a sample from your nose or throat in this scenario.
- Nasal aspirate — a saline solution will be injected into your nose, and a sample will be collected with a mild suction.
- In a tracheal aspirate, a narrow tube with a torch, sometimes known as a bronchoscope, is inserted into your mouth to reach your lungs, where a sample is taken.
- Sputum Test – Sputum is a thick mucus that builds up in the lungs and is coughed out. During this test, you’ll be asked to cough up sputum into a specific cup or have a sample taken from your nose using a swab.
- Blood test – A blood sample is collected from a vein in the arm in this scenario.
- Antigen detection-based rapid diagnostic testing
- The COVID-19 has also been subjected to a fast test, which entails obtaining samples from the nose, throat, and lungs. The viral proteins (antigens) associated with the COVID-19 virus may be detected using a rapid diagnostic test (RDT) of a sample of a person’s respiratory tract. This assures a quick and accurate diagnosis, and the CDC has authorized its use.
Rapid diagnostic methods based on the identification of host antibodies
This test looks for antibodies in the blood of patients who have been infected with COVID-19. The intensity of an antibody response is influenced by a number of variables, including age, drugs, infections, and the severity of the condition.
The worried health experts may urge you to wear a mask during the exam before you begin. The healthcare expert may inform you whether there are any further actions that need to be performed.
What are the potential dangers of testing for Coronavirus?
When the swab is put into your nose and throat, you may experience a choking feeling. The nasal aspirate, in particular, may be unsettling. All of these side effects, however, are very transitory and will go away soon after the test. There may be bleeding or infection after a tracheal aspirate. There are no dangers associated with the blood test. There may be some swelling and soreness in the place where the needle was inserted, but this will go away quickly.
What should you do if the Coronavirus test is positive?
If your test results are positive, you might be infected with the coronavirus. Although there are no particular therapies for coronavirus infection, your healthcare provider may recommend certain measures to assist you manage your symptoms.
You may take the following actions to help alleviate the symptoms:
- Getting enough of fluids
- Getting enough sleep
- Using OTC (over-the-counter) medications
- If your illness worsens or you develop indications of pneumonia, you should seek medical attention. Severe cough, labored breathing, and a high temperature are all frequent pneumonia symptoms.
- If you’ve been diagnosed with coronavirus, you should take the following precautions to prevent the virus from spreading:
- Do not leave the house unless you need medical assistance.
- When you’re in public or among other people, always wear a face mask.
- Personal goods such as drinking cups, plates, towels, and other objects should not be shared with others.
- Always thoroughly wash your hands for at least 20 seconds. If soap water is not available, an alcohol-based sanitizer containing at least 60% alcohol may be used instead.
- Whether your findings were negative, you should consult with your doctor to see if any more testing is necessary. It’s preferable to take safeguards rather than risk spreading the sickness.
You may, on the other hand, prevent being infected with coronavirus by following the measures below:
- In the absence of soap-water, wash your hands thoroughly for 20 seconds and apply alcohol-based sanitisers.
- Keep your hands away from your eyes, nose, and mouth.
- If at all possible, stay away from persons who are sneezing or coughing.
- Using a disinfectant spray, clean regularly handled home objects.
When should you seek medical help?
There is no need to see your doctor if you have minor symptoms such as a slight temperature or cough. Keep an eye on your symptoms, isolate yourself, and remain at home. If you live in one of the COVID-19 hotspot locations, don’t dismiss fever symptoms if they last longer than three days. Seek medical assistance right away. In any event, while going outdoors or seeing a doctor, always wear a mask. Maintain a 6-foot separation from other individuals and avoid touching surfaces with your hands. If you’re having trouble breathing or have discomfort and pressure in your chest, see a doctor.